Copy .iso image to USB flash drive using dd command in Linux using the terminal
ID: 119
Category: Linux Terminal
Added: 3rd of September 2019
Updated On: Tutorial updated and rechecked on 10th of December 2024
Views: 5,817
Related Tips & Tutorials
➔
Create a multiboot USB for your .iso images, using Ventoy on Linux
If you are intending on installing a new Linux distribution on your system, you will need to download the .iso file and write this to a USB flash drive. There are various applications that allow you to do this in Linux, but another way is to use the dd command in the terminal.
The first thing to do is plug in your USB flash drive and get the path to your USB flash drive. Enter the following command.
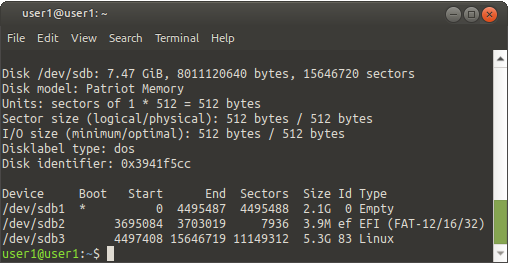
sudo fdisk -l
Mine is listed as
/dev/sdb 7.5 GiB which is my PATRIOT flash drive.
Next we need to enter the following command to write to the .iso file to the USB flash drive.
My download .iso file can be found in my Downoloads directory.
We are writing this to
/dev/sdb which is the Flash drive.
sudo dd if=Downloads/xubuntu-whatever.iso of=/dev/sdb bs=1M status=progress
The bs command specifies the block size, in this case we set it to 1M (1 Megabyte). The default size is set to 512bytes.
status=progress is self explanatory, it shows you how much data is being written to the drive.
After writing the .iso file to your USB flash drive, you need to reboot your machine enter bios mode and set the boot order priority to your USB flash drive. After saving the setting and rebooting your machine, your new Linux distribution will then boot in to live mode.
For further information on .iso images please visit wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ISO_image